Unsupervized Image Cateogorization using Word Embedding
16 May 2018 | Machine Learning Computer Vision Word Embedding
Social media is flooded with various categories of photos: food, travel, selfie, etc. Unless the user explicitly mentions, the category of the photos uploaded is left unknown. For the purpose of creating meaningful value from the social media photos, it might be useful to have a scalable model to classify which category each photo belongs to.
For this particular problem, using a supervized learning algorithm might not be scalable for several reasons:
- Supervized learning requires large dataset to train on, but it is hard to acquire large quantity of social media photos due to privacy issue.
- Even if there is such dataset available publicly, it is unlikely that it also contains image category labels.
- EVEN IF there is both data and labels available, hauman-labeled categories suffers risk of biasness. Some of the photos could sit in between two possible cateogries, who gets to decide which?
Hence, using supervized learning algorithm is not a smart choice for this case, which leaves unsupervized learning algorithm pretty attractive option.
The unsupervized image categorization takes a couple of data processing steps:
- Image item labelling using Google Cloud Vision API
- Vectorization of images using Word2Vec
- Clustering the image vectors by K-Means algorithm
1. Image item labelling using Google Cloud Vision API
Google Cloud Vision API provides labels for items appeared in the image together with the probability and topicality values. Probability value indicates how accurate the given label is to each item, and topicality value indicates the significance of the item with respect to the rest of the items inside the image.

After running the Image Labelling API through each image, I have a list of item labels and their respective probability and topicality vales which are float numbers in between 0 and 1. These two values are used in the next step for weighting image vectorization using word embedding.
2. Vectorization of images using Word2Vec
Using the item labels for each image, the algorithm then imports pretrained Glove Word2Vec model to convert image labels into vectors. Each word vector is further weighted by the coresponding probablity and topicality values by multiplying them. Since there are generally more than one label for each image, the algorithm averages word vectors assigned for each image, producing a single centroid vector that best describe what the image is about. In the end, each image is converted to a numberical vector, so that it can be processed by Uclidean arithmetic.
3. Clustering the image vectors by K-Means algorithm
Once all images are converted to vectors, the algorithm applies K-Means algorithm to cluster images with similar characteristic, which is bascially the type of items it contains inside.
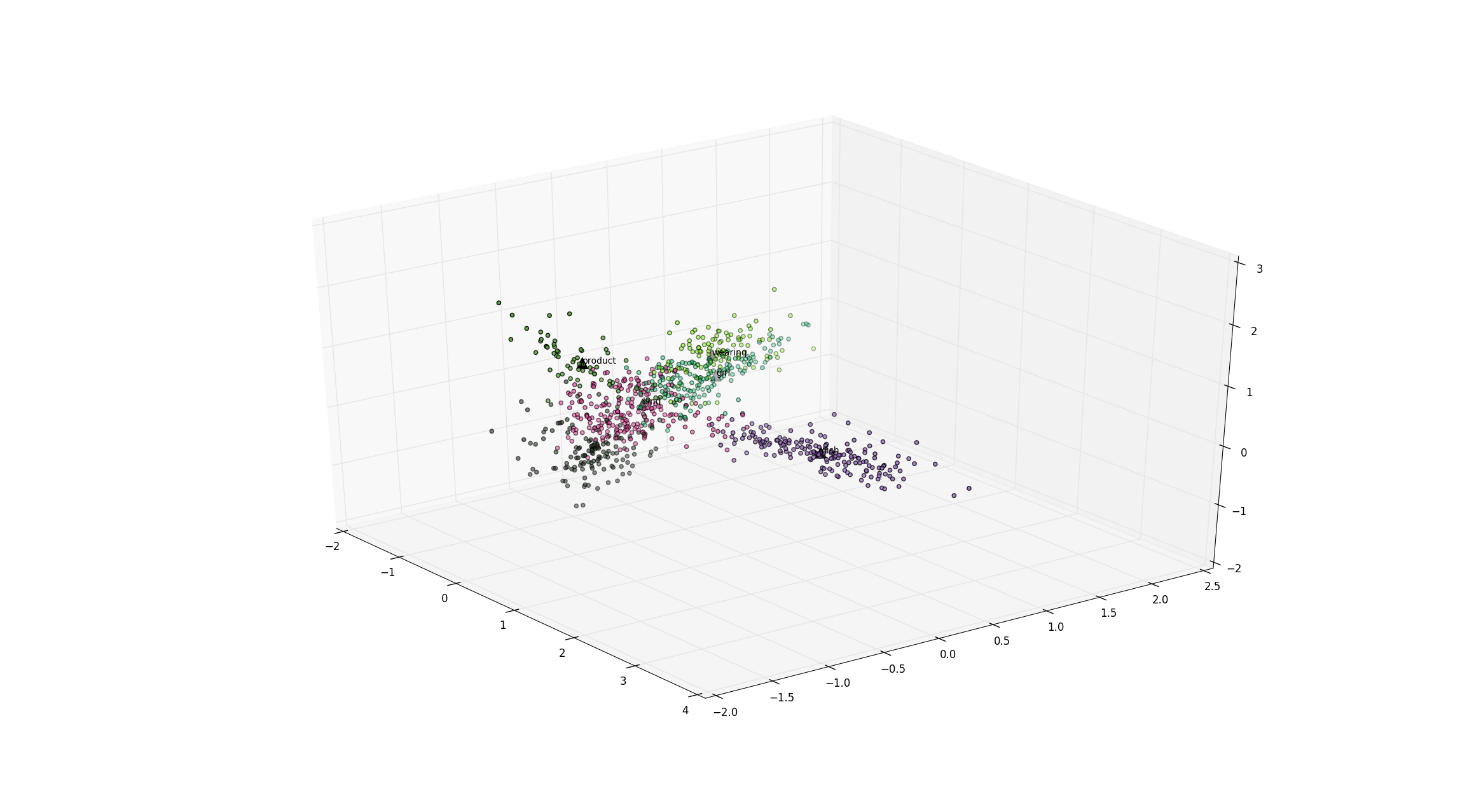
The figure above is the visualization of the image vector space whose dimension reduced to 3, using Principle Component Analysis (PCA). The data points with the same color indicate that they belong to the same image category. In order to know what each image category represent, the programme finds the centroid vector for each image cateogry and look up the Word2Vec model to list words with the closest distance.
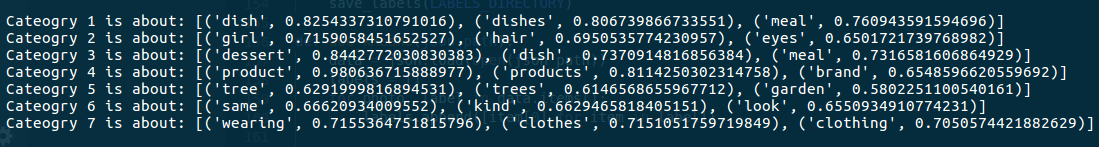
As shown by the print message, it is pretty obvious that cateogry 1 contains images related to food, while category 7 contains images related to clothings and fashion. Initially, the dataset contains uncategorized images scraped from Instagram such as these,
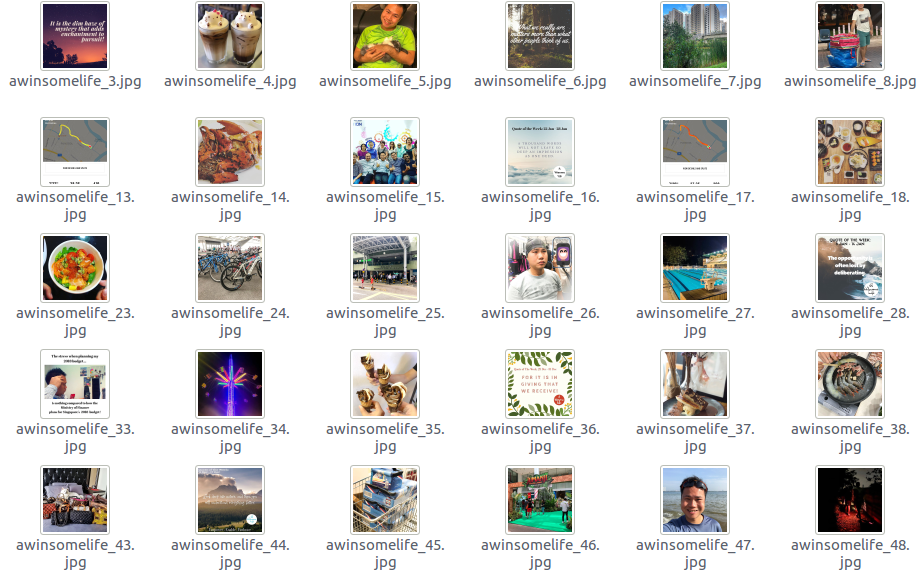
and classify them into arbiturally genrated categories such as food,

products,
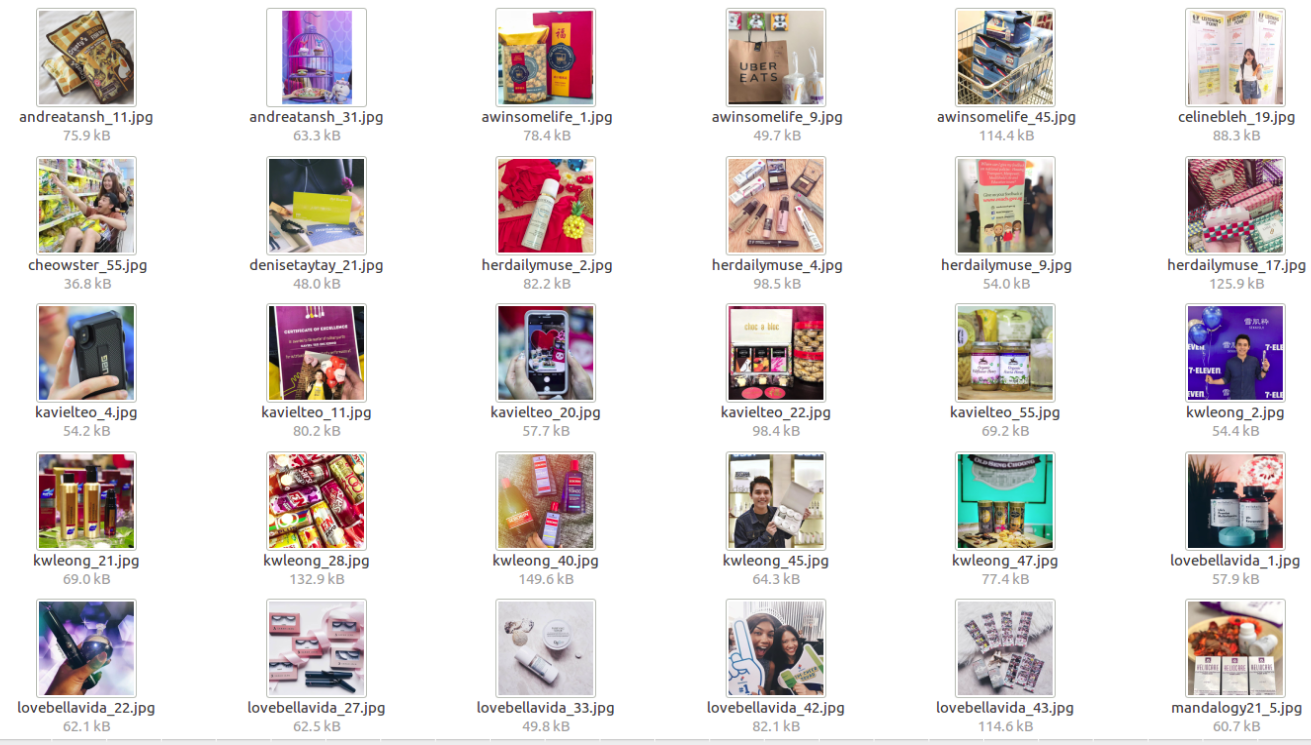
and travel.
Summary
This technique categorizes image dataset into a couple of arbitrary topics, based on the items spotted in each image. It first labels item labels inside each image, convert them into semantic vectors, and cluter them using K-Means algorithm. Bare in mind that the accuracy of the categorization is dependent on the accuracy on the Google Cloud Vision API and the pretrained Word2Vec model. There were few outlier images which did not give out any label when run on Cloud Vision API Labeling, which are better to be excluded out and categorized as “No Cateogry”.
As described above, this technique is an unsupervized learning algorithm. This means that instead of setting the categories and classifying each image into respective category, the algorithm classifies all the images first then label each image cateogry based on the common characteristics of clustered images.